School of Social System Management Gifu University
Bringing innovation to management
Training personnel with practical competency
*Information related to faculty members/students and graduate schools at Gifu University here are all that of the time of interviewing.

Essential for local revitalization
Education in the field of business management
Gifu University includes the Faculty of Education, Faculty of Regional Studies, School of Medicine, Faculty of Engineering, and the Faculty of Applied Biological Sciences, and has conducted education and research in a wide range of fields. As a university based in Gifu Prefecture, it plays a major role in contributing to local development and regional revitalization.
However, something seems to be missing to fully fulfill this role. As a solution, we identified "education in the field of business management." We could further enhance our ability to contribute to regional revitalization by adding a management perspective to the research results accumulated by the Faculty of Engineering and the Faculty of Applied Biological Sciences.
What encouraged us were the earnest voices of local stakeholders. In addition to economic organizations such as the Gifu Employer's Association, the Chamber of Commerce and Industry, and the Japan Association of Corporate Executives, we also received strong requests from the Gifu Prefecture Senior High School Principal Association and Senior High Schools for a place to train human resources to contribute to regional revitalization and for personnel in the management field. Gifu Prefecture is experiencing a rapidly declining birthrate, an aging population, and declining industries. Furthermore, Gifu has also faced natural disasters in recent years, and there is a need for human resources who can practically resolve the various issues the region faces. In light of this situation, we established a working group in 2016 to establish an organization to provide education in the field of business management. In April 2018, a preparatory office was set up for the establishment of a new faculty and has been steadily making preparations.
Until now, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) has promoted "Faculty" programs for undergraduate courses. However, as a result of the systemic revision in August 2019, the university establishment standards have changed, establishing the new system of "joint undergraduate courses." This system allows for the establishment of a new educational organization on the condition that two or more faculties collaborate, utilizing existing resources of the university such as faculty and facilities.
Gifu University was recently planning to establish a business management field. However, although we considered a variety of proposals, including opening a new faculty, we concluded that all of them are difficult. At the time, it was decided to establish the new joint undergraduate system, and it was agreed to use this system to establish an organization.
Although the decision to establish the new organization in the field of business management was made, the name of the organization became an issue. If it was not a "Faculty, "what should it be called? After multiple discussions with MEXT, the university was allowed to suggest its own name. Gifu University produced numerous options, and as a result of careful consideration, "School of Social System Management" was decided upon as the name.
The title "School of" may be unfamiliar to some students, so pamphlets and other materials always include the world "undergraduate equivalent" after the title. Students attend for the entrance examination to enroll into the School, and graduate after four years of study. In this respect, they are no different from the students enrolled into a Faculty. The greatest difference is that it uses existing university facilities and is composed of Faculty members who hold concurrent positions in other faculties. All 14 faculty members are full-time members of the School of Social System Management, 13 of whom also belong to other faculties and are in charge of other class subjects.
The name is already in use at graduate schools of other universities, but this is Japan's first educational organization to offer undergraduate courses under the joint undergraduate system.
Emphasizing the perspective of SMEs
Teaching business management that leads to regional development

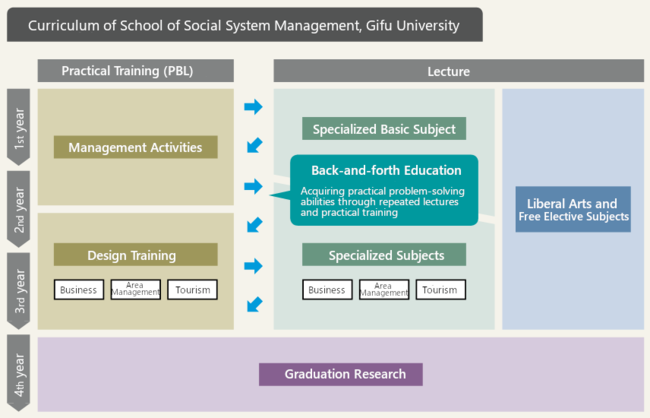
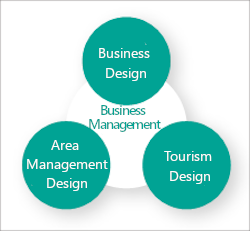
We believe that many of the issues facing Gifu Prefecture can be summarized into three categories: Business Design, Areal Management Design, and Tourism Design. Accordingly, the School of Social System Management will develop a management-based curriculum while focusing on these three fields. In their first and second years, students will learn about business administration, which is the cornerstone for delving deeply into the aforementioned three areas. From the second semester of the second year, students can select one from Business Design, Area Management Design, and Tourism Design to tackle more specialized issues from the perspective of management. In the first semester of the third year, students begin specialized seminars, where they are assigned to a specific faculty member akin to a graduation research supervisor and acquire knowledge on a deeper level.
Business administration, as we know it today, was born in the US in the 19th century, with the emergence of the huge market due to construction of railroads allowing free traffic. As large corporations grew along with this, business schools began to teach management to train managers. In the US, graduation from a business school is important to advance your career. As a society where career advancement is talked about as a set of qualifications, it is very different from Japan, where you grow within the company where you are employed.
A major characteristic of Japan is that most of the companies that support the economy are small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). SMEs, including private businesses, account for 99.7% of all companies and nearly 70 percent of the total number of employees. Many SMEs support the livelihoods of local people. In the context of contributing to the revitalization of Gifu Prefecture, we would like to focus on SMEs and teach business administration that will lead to the creation of local communities.
As a result of the spread of the coronavirus pandemic, the way that Japanese people work has begun to change dramatically. The era of working in a single company for many years is over, and society is changing to realize more flexible ways of working, including second jobs. It is time to successfully extend networks both inside and outside the company to smoothly promote projects. Our goal is to teach management that responds to these times with individuality.

Learning business administration not just at the desk, but practically out in the field

Traditional management was basically classroom study. It is something you learn at a desk, without going to actual companies or local governments. Our mission, however, is to produce human resources who can specifically tackle the issues facing the region. Therefore, the curriculum of the School of Social Systems and Management includes two 18-month long internships (total of three years). The aim is to have students learn in the field while maintaining the basics of business administration. They will experience firsthand the current issues facing the field, and as the next step, they will put efforts to solve these issues into practice.
Between the first and third years, students will continue long-term training in two separate sessions. In a regular university class, such training is almost always terminated in half a year, but the advantage of working on practical training over a year and a half will allow students to build experience. First, half a year of practical training is carried out. After verifying the results, it can then expand to a new approach in the next half year. We call this the continuous development type, and it does not end with a one-shot but cultivates the ability to tackle a variety of issues in a step-by-step manner.
Our goal is to practice project-based learning (PBL). It is also referred to as "problem-based learning," where students visit companies and local governments to determine the problems from the people involved, and then discuss and implement solutions. This is practical training for PBL. A total of one-and-a-half years of practical training in this way will certainly produce results. For example, we would like to develop a "return results" type of practical training where we will always give back results, even if they are small, such as "developing a product label" or "finding improvement in the work."
The Management Activity Practical Training conducted between the first and second years overlaps between the first- and second-year students, and the three Design Practical Training elements (business, area management, and tourism), which begin in the second semester of the second year, overlap for the second- and third-year students. It is known as "mixed education." During this, students from different years study together, depending on how their practical training progresses, and students with experience and those who are working for the first time discuss and perform group work while confronting each other's perspectives. The older students will have already gone through the content, so they will naturally be on the teaching side, which will give them a different motivation to attend practical training.
To Develop a Multifaceted Perspective
Cross-Faculty Education and Reciprocal Education.
Practical training requires coordination with companies, local governments, and various organizations. To date, this has been done by individual faculty members, but one of the unique features of the School of Social System Management is the establishment of regional councils so that practical training is carried out more smoothly.
The regional council is an organization that invites outside parties to participate and provide their opinions on the assembly, operation, planning, implementation, and results of the practical training. Currently, six members of the Gifu Prefectural Government and private companies in the prefecture have been selected as council members. However, in the future, we would like to create an open forum where more people from companies can freely participate and actively discuss the practical training and education we provide. We would also like to have various external evaluations of both the curriculum in general and the practical training.
The major characteristics of the curriculum are "cross-faculty education" and "back-and-forth education." Until now, there was a system for students to voluntarily take courses that they were personally interested in from other faculties. The cross-faculty education program at the School of Social System Management incorporates classes from other faculties within its curriculum in advance. Of a total of 82 subjects, 20 are from other faculties, which accounts for a significant proportion. The challenges that the region faces span multiple fields. Therefore, our aim is to encourage students to develop a multifaceted way of thinking and knowledge through cross-disciplinary learning from other faculties. It also includes classes in collaboration with the School of Economics, Nagoya University.
Another distinctive feature of the program is that lectures, practical training, and exercises are not conducted in isolation, but in conjunction with each other. In other words, after attending a lecture, students participate in practical training and attend other lectures based on their knowledge. In this type of education, the knowledge from lectures is utilized in practical training, the learning from practical training is theorized in lectures, and then put into practice again in practical training, thus achieving high educational effectiveness.
With a view to fostering successors and entrepreneurs within family businesses
As an organization that only started in April 2021, our primary goal is to turn the "pie in the sky" into reality and steadily implement the contents that were included at the time of establishment. We would also like to establish paths for graduates to find employment.
We envision general employment opportunities for liberal arts students, such as private companies, financial institutions, and local governments, both locally and outside of the prefecture, but we are also considering training successors to family businesses and producing entrepreneurs. In the field of tourism, destination management organization (DMO), which are well versed in local tourism resources, are attracting attention as corporations producing tourist attractions in cooperation with the local community. Students at the School of Social System Management are involved in visiting various companies and local governments in the region through practical training. Through these experiences, the students are expected to become familiar with a lot of companies and governments. We believe that these experiences will also help prevent mismatches when it comes to employment.
We are also looking forward to establishing a graduate school in the next four years. Although no concrete plan has been developed yet, we would like to create a place where diverse human resources can study together, not just those graduated from the School of Social System Management and continuing their education, but also working adults and international students.
Recently, MEXT has issued a policy to allow local universities to increase their capacity, and we would like to consider increasing capacity while making successful use of this policy.
In addition, we are considering providing training courses to develop organizational leaders for working adults, as well as training programs for the development of young human resources at corporations. Working hand in hand with the local residents, we would like to contribute to the solution of the various issues of Gifu Prefecture.
What is Design Thinking Education?

Assistant Professor
Mayumi Kawase
Design Thinking Theory
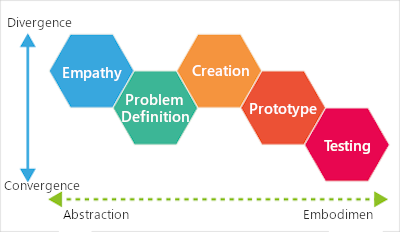
Stanford University Design School, Five Steps of Design Thinking (partially modified).
By tackling the challenge according to these five steps, students can create ideas with
a thinking process similar to that of a designer, even if they have not studied design
professionally. In design thinking, students learn this way of thinking about problem
solving.
"Design" in design thinking refers to a slightly more abstract sense of the word, not just appearance. Gifu University aims to identify the nature of problems occurring around people, set issues, conceive and realize desirable conditions, and improve its ability to analyze issues in the current situation, and in particular, to identify issues in groups.
Gifu University has already developed classes incorporating design thinking in courses such as "Introduction to Design Thinking," a required course for first-year students at the Graduate School of Natural Science and Technology, but the School of Social System Management focuses on community design in particular. While acquiring the ability to understand what is happening in community settings and to define problems, we also aim to develop local management leaders with design and management skills by putting them in the field where challenges arise.
INTERVIEW

Professor
Shigenori Maezawa
Organizational Leadership Theory
As a specially appointed professor, I am involved in the education at the School of Social System Management. Over the years, I have been deeply involved in the field-oriented distribution studies at the Faculty of Applied Biological Sciences. With a field-oriented attitude, we can sense social changes in real time, and our sense of values evolves. We tend to focus on obtaining information from textbooks and materials and remembering the correct answers in the classroom as classroom learning, but there is another world in society that we cannot decern from such learning. At the School of Social System Management, the combination of classroom learning and off-campus practice is structured to induce new awareness and behaviors.
Many university students seem to be in a state of mind where they do not have major complaints about their life, but want to spend their days more satisfactorily, or do not know what to do. To clear this feeling of confusion, do something small, something you can do right now and enjoy the feeling of accomplishment. For example, regularly doing things such as sitting at the front in lecture rooms or asking professors a question in AIMS* in one lecture every day can produce results. These results will produce confidence, developing a habit of taking on new challenges, and creating a sense of fulfillment.
At the School of Social System Management, you can achieve student life that you can truly appreciate.
※AIMS: Systematic fieldwork (PBL training) to support student learning at Gifu University
INTERVIEW Business Design Program

Visiting local companies to learn about actual situations and to acquire applied skills for the real world

| Associate Professor Kimio Shibata Marketing Theory |
Associate Professor Osamu Ichikizaki Production and Operations Management |
Professor Atsumi Kato Business Administration |
Professor Shigenori Maezawa Organizational Leadership Theory |
In the Business Design Program, students learn about business and management, that is, how to efficiently utilize management resources, such as human resources, goods, money (capital), and information, to achieve goals. In the one-and-a-half-year Business Design Practical Training, which is the core of the program, students learn the process of defining real problems, analyzing the root causes, and developing solutions. For example, in agricultural business, there are many players, such as farmers, agricultural cooperative union supporting farmers, restaurants or inns using the ingredients. In the practical training, the first step is to grasp the whole picture of the business and to understand what kind of players are acting. Then, the next step is to focus on a specific organization such as farmers or retailers, and to develop a solution, by researching their business and management and having discussions with people related to the organization.
Connected with the practical training, students also learn the fundamentals of business and management such as design thinking, project management, and management strategy in the first semester. Then students study more specialized areas such as financial statements analysis, risk management, and production management in the second and third semester. In the end of the practical training, students make presentations of their achievement.

We believe the "on-site experience," such as visiting actual companies and finding problems by themselves, is essential. There are many different industries and types of companies. The most important thing is to know them firsthand, and we hope that, by gaining awareness at real workplaces, students will acquire applied skills to be useful in the real world.
INTERVIEW Area Management Design Program

Students will be involved in three student-led activities, including the planning of promotional strategies for FC Gifu.

| Professor Akiyoshi Takagi Area Management |
Professor Yoshifumi Demura Urban History, Landscape Management |
Associate Professor Younmi Lee Economics and Agriculture |
In the Area Management Design program, students learn how to create work that creates value for the place by considering sustainable regional management in which various positions collaborate.
In the Area Management Design practical training, students simultaneously work on multiple projects. In the first year they work on activities such as the promotion strategy of FC Gifu, a professional soccer club, and the community revitalization project developed by Kamoken Lab, an LLC in Minokamo City, Gifu Prefecture from local energy management to renovate vacant houses in front of the station. By focusing on a main project and participating in other projects, we intend to provide multifaceted learning through actual experience.

In addition, the faculty members involved in the area management design exercise are also involved in various projects in Gifu Prefecture. Students can experience various challenges rooted in the community. To promote administrative policies through identifying issues in Gifu City, to participate in some collaborative businesses in the Yanagase shopping district, to get involved in community development leading to construction of the roadside stations, and to revive farmland abandoned due to no owners, are examples ready to start. In addition, through lectures, such as risk management and public management, students can learn deeply about the problems and general solutions, relating to actual challenges in their experiences.
Solving the challenges in community development cannot proceed in the absence of the people involved. It is important to visit the sites and listen to the voices of the parties concerned to make sure the essence of the issues. The program aims to nurture human resources with the ability to respond to situations and an entrepreneurial spirit that can be used in any field by gaining experience in extracting issues and developing experiences to edit business by utilizing management perspectives.
INTERVIEW Tourism Design Program

Students plan and carry out a two-night, three-day sightseeing tour, and cultivate their planning skills through hands-on experience.

| Professor Sakae Mitsui Econometrics |
Associate Professor Junji Moribe Biological Resource Conservation |
Associate Professor Keijiro Okuoka Environmental Systems Engineering |
Professor Mutsuki Higo Satoyama Conservation |
In the Tourism Design program, students focus on the value created by tourism and aim to acquire the skills to build a regional brand using local resources and to plan tourism-related activities.
In the Tourism Design practical training, Gifu Prefecture is used as a tourism model, and students begin learning about the local resources in the prefecture. In the second semester of the second year, they actually visit the area and explore the local resources that can lead to business by excavating the culture and history of the area. From the first semester of the third year, they devise a two-night three-day sightseeing tour assuming that tourists will stay in the region. In the past, we have tried to plan similar tours in the specialized seminars of the Faculty of Regional Science, but the School of Social System Management takes this further and develops it to the point of implementation. To lead a successful tourism business, it is very important to clarify the target audience that you want to attract. Based on previous analyses, students develop plans for specific processes and budgets, and by implementing the plans with local bus companies and travel agencies, they will not end up with empty theories on the table but learn from various real-life experiences. In addition, students will study a wide range of tourism-related fields through lectures on tourism, Satoyama conservation, regional design, and resource management, and will further deepen their learning through repeated classroom and practical training.

The distinctive feature of the Tourism Design program is that students can comprehensively learn a wide range of fields rather than specializing in tourism studies. Through this program that cultivates multiple perspectives, we wish to develop human resources that can contribute to the community by engaging independently in various issues and contribute accordingly.